-
Home
-
Products
-
Application
-
Documents
-
News
-
Blog
-
Blog
-
Sinsegye
Leave Your Message
-
Wechat OA

-
 Baijia Hao
Baijia Hao



 Baijia Hao
Baijia Hao

Choosing the right Motor Driver for your project can be challenging. Motor Drivers are essential components that convert signals from your microcontroller to control motor functions. They enable precise movements in robotics and automation.
Consider your project requirements carefully. The kind of motor you are using matters. Different Motors require different types of Motor Drivers. For example, DC motors need a different driver than stepper motors. A common mistake is overlooking voltage and current ratings, leading to potential failures.
Selecting a Motor Driver often involves compromises. You may not always find the perfect fit for every need. Analyze your budget and performance criteria. It’s crucial to test multiple Motor Drivers to determine their real-world effectiveness. Reflection is necessary as you fine-tune your choices.
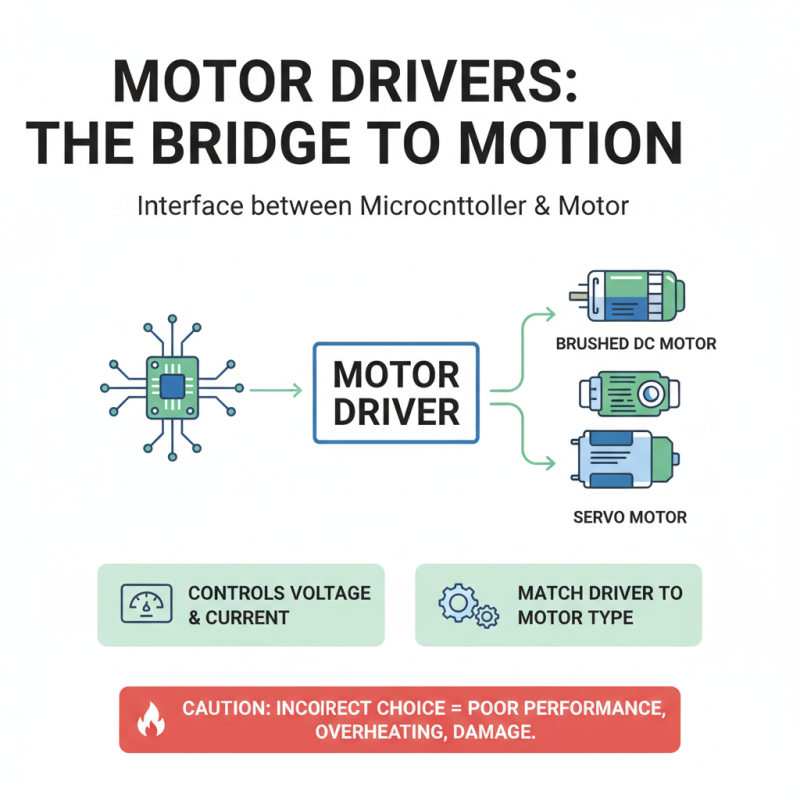
When starting an electronics project, understanding motor drivers is crucial. A motor driver is an interface between a microcontroller and a motor. Its main job is to control the voltage and current flowing to the motor. Different motors require different drivers, so it is essential to match them correctly. If you make a wrong choice, the motor may not run effectively. It might overheat or even get damaged.
Tips: Always check the specifications of your motor. Know its voltage and current ratings. This knowledge guides you to the appropriate driver. Also, consider the type of control you need. Do you want simple on/off control, or do you need speed variation? Drivers can vary significantly based on your requirement.
It may be tempting to choose the most powerful driver available. However, you should think about efficiency too. An overpowered driver can result in wasted energy. It might also complicate your design and increase costs. Sometimes, a simpler solution meets your needs without excess power. Reflect on what is truly necessary for your project.
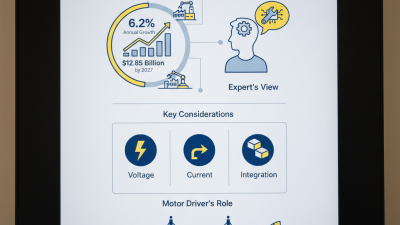
When selecting a motor driver, understanding the types is crucial. There are several categories, each suited for specific applications. For example, DC motor drivers are popular in robotics and automotive applications. They provide effective control over speed and direction. Reports indicate that the demand for such drivers is estimated to grow by 8% annually through 2025.
Stepper motor drivers serve a different purpose. They excel in precision tasks, like 3D printing and CNC machines. Their ability to move in fixed steps allows for accurate positioning. A recent industry analysis showed a significant increase in stepper driver usage, projected to reach 30% of the motor driver market.
Brushless motor drivers are gaining traction in applications requiring high efficiency. This includes drones and electric vehicles. They often come with advanced control algorithms, enhancing performance in variable environments. However, their complexity can lead to integration challenges. Many engineers might overlook compatibility, potentially causing delay in projects. It's vital to assess these factors thoroughly.
When selecting a motor driver for your project, several key factors come into play. Voltage ratings should match your motor specifications. A mismatch can lead to inefficiency or damage. Additionally, consider the current capacity. Overloading a driver can cause failure, while underloading may not meet performance demands.
Control methods are also crucial. Some projects may require PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) for speed control, while others might need directional control. Understanding your project's specific requirements will guide your choice. Don't forget about thermal management. A driver may heat up during operation, and insufficient cooling can shorten its lifespan. Use heat sinks or cooling fans where necessary.
Finally, think about ease of use. Some drivers come with detailed documentation, making integration simpler. Others might be challenging, leading to potential frustration. Reflect on your skills and resources. Opt for a solution that matches your expertise and project complexity. Balancing these various factors can determine the success of your project.
This chart compares various specifications of three hypothetical motor drivers. The dimensions considered include current rating, voltage rating, PWM frequency, and control type, helping users choose the right driver for their projects based on specific needs.
When evaluating power requirements for motor drivers, it's crucial to consider the
voltage and current ratings.
Typically, motor drivers operate within a specific range. For instance, a common DC motor may require
12V and draw 2A. Properly matching these specifications ensures
reliability and optimal performance.
In the 2022 industry analysis by TechInsights, approximately
40% of projects failed due to power compatibility issues.
Many engineers overlooked the peak current demands during startup. This oversight can lead to
overheating and potential damage.
When connecting a motor driver to your project’s components, precise wiring is essential. Start by identifying the input pins on the motor driver. These pins will link to the control signals from your microcontroller. Each connection must be secure to avoid intermittent issues. Use solid wires for reliable connections.
Next, connect the motor terminals. Ensure you know which direction the motor will spin. You might need to swap the terminals if the motor runs backward. This trial and error can be frustrating but is often necessary. Remember, an incorrect connection can lead to motor stalling or overheating.
Power supply is another crucial factor. Ensure the voltage matches what the motor driver requires. Too low, and the motor won’t run. Too high, and you risk damaging components. It’s helpful to use a multimeter to verify voltages. Don't rush the setup, as careful testing prevents future pitfalls.
Always double-check every connection before powering on the system. Even small oversights can result in major setbacks.