-
Home
-
Products
-
Application
-
Documents
-
News
-
Blog
-
Blog
-
Sinsegye
Leave Your Message
-
Wechat OA

-
 Baijia Hao
Baijia Hao



 Baijia Hao
Baijia Hao

In the realm of automation systems, precise control of motion and speed is paramount for optimal performance and efficiency. This is where the concept of a "Servo Drive" comes into play. A Servo Drive is an essential component in modern automated machinery, responsible for controlling the operation of servo motors by regulating their speed, position, and torque. As industries increasingly adopt advanced automation technologies to enhance productivity, understanding how a Servo Drive functions becomes crucial for engineers and technicians alike.
At its core, a Servo Drive interprets commands from a controller and sends the appropriate electrical signals to the motor. This feedback loop allows for real-time adjustments, ensuring that the motor responds accurately to the desired parameters. The ability to achieve high levels of precision makes Servo Drives indispensable in various applications, from robotics and CNC machinery to conveyor systems and packaging processes. As this technology continues to evolve, the integration of Servo Drives into automation systems is set to revolutionize manufacturing practices, leading to smarter, more responsive industrial environments that cater to the demands of today’s fast-paced economy.


A servo drive is a crucial component in automation systems, primarily designed to control the motion of servo motors, which in turn drive mechanical systems. It integrates control algorithms, feedback devices, and power electronics to achieve precise position, speed, and torque control. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global servo drive market is projected to witness a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% from 2021 to 2026, highlighting the increasing adoption of automation technologies across various industries, including manufacturing, robotics, and aerospace.
In automation systems, servo drives function by processing signals received from a controller, adjusting the output to the motor accordingly. This closed-loop control system relies on feedback from encoders or resolvers to ensure that the servo motor operates within predefined parameters. Research from Technavio indicates that advancements in digital signal processing and improved sensor technologies are driving innovations in servo drive functionalities, enabling higher efficiency and better performance in applications ranging from CNC machinery to automated assembly lines. The continuous improvements in servo drive technology not only enhance precision but also reduce operational costs, making them integral to modern automation solutions.
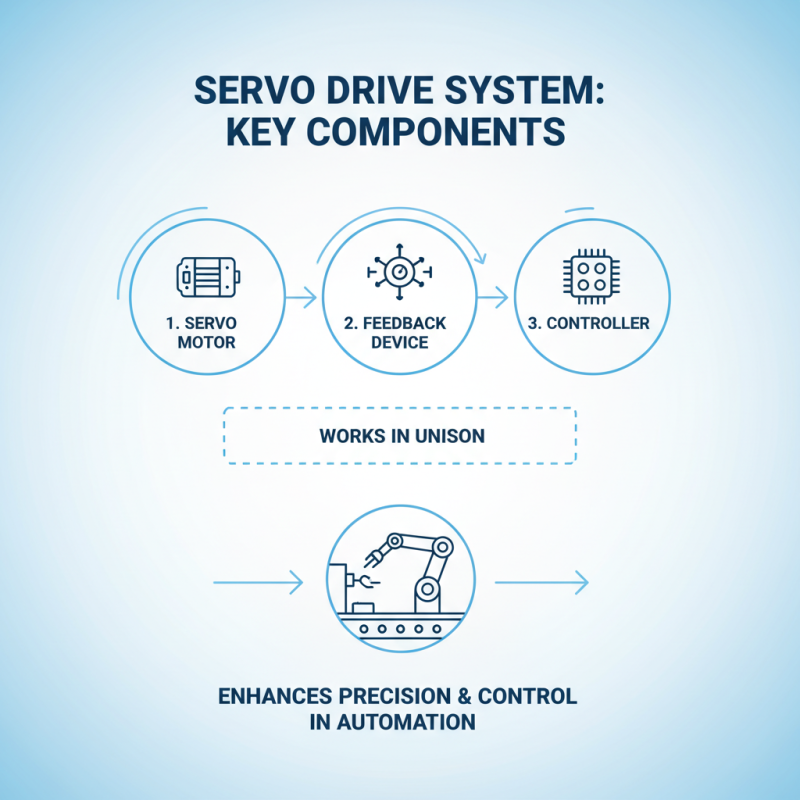
A servo drive is an essential component in automation systems, playing a critical role in enhancing precision and control in machinery. The key components that constitute a servo drive system include the servo motor, feedback device, and controller. Each of these elements works in unison to ensure accurate positioning and movement of various automated processes.
The servo motor is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, providing the necessary torque and speed required for precise movements. Feedback devices, such as encoders or resolvers, continuously monitor the motor's position and speed, relaying this information back to the control system. This real-time feedback is crucial for maintaining accuracy, allowing the system to make instantaneous adjustments to the motor's performance.
The controller serves as the brain of the servo drive system, processing the feedback from the motor and sending commands to achieve the desired motion profile. It utilizes complex algorithms to adjust the pulse width modulation (PWM) signals that drive the motor, ensuring smooth and accurate operation. Together, these components create an efficient and responsive system, essential for modern automation applications in various industries.
Servo drives play a crucial role in automation systems by converting commands from a controller into precise movements in machinery.
The control mechanism behind servo drives is based on feedback loops, which allow for real-time adjustments during operation.
When a command is given—such as moving a robotic arm to a specific position—the servo drive uses sensors to monitor the actual position and speed of the motor.
This data is fed back to the drive, enabling it to calculate the difference between the commanded position and the current position, known as the error.
The servo drive then adjusts the motor's output to minimize this error, ensuring accurate and smooth movement.
Tips: To enhance the performance of your servo drive system, ensure that the feedback sensors are calibrated correctly.
Regular maintenance of the drive and motor can also prevent discrepancies that may affect the system's overall efficiency.
Additionally, the control algorithms used in servo drives can vary, with common types including proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controllers.
These algorithms help in optimizing the response time and stability of the system. By fine-tuning the parameters of these controllers, engineers can achieve better performance in dynamic applications, where quick response and precision are essential.
Tips: Experimenting with different control algorithm configurations can lead to improved motion control.
Consider running simulations to identify the best settings before implementing changes in a live environment.
Servo drives play a crucial role in automating processes across various industries by enabling precise control of motors and movement. In manufacturing, for example, servo drives are commonly used in robotics and assembly lines, where they enhance the accuracy and speed of operations. By adjusting the position, velocity, and torque in real-time, servo drives ensure that machinery operates seamlessly, leading to increased productivity and reduced waste. This precision is especially beneficial in industries such as automotive and electronics, where component alignment and placement are critical.
In addition to manufacturing, servo drives find applications in the packaging industry, where they contribute to the efficient operation of conveyor systems and packaging machines. Their ability to synchronize movements allows for smooth transition between different stages of packing, from filling to sealing. Furthermore, in the aerospace sector, servo drives are integral to controlling the various actuator systems that manage flight control surfaces, demonstrating their versatility in critical applications. Overall, the adaptability of servo drives to different settings makes them indispensable in enhancing operational efficiency across multiple sectors.
| Industry | Application | Benefits of Servo Drives | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Robotic Automation | High Precision and Speed | Pick and Place Operations |
| Automotive | Conveyor Systems | Improved Control and Efficiency | Assembly Line Operations |
| Aerospace | Flight Simulation | Precision Movement | Simulating Flight Conditions |
| Textile | Weaving Machines | Enhanced Fabric Control | Automatic Loom Operations |
| Food Processing | Packaging Machines | Increased Production Rates | Sealing and Filling Applications |
Servo drives play a crucial role in automation processes by providing precision control over various types of machinery and equipment. One of the primary benefits of using servo drives is their ability to deliver high accuracy in motion control. This precision is essential in applications requiring exact positioning and repeatability, such as robotic arms and CNC machines. By utilizing closed-loop feedback systems, servo drives continuously adjust their output based on real-time data, ensuring that each movement aligns perfectly with the desired specifications.
In addition to their accuracy, servo drives enhance the efficiency of automation systems. They contribute to reduced cycle times, allowing equipment to operate faster without sacrificing performance. Moreover, the inherent energy efficiency of servo drives helps minimize power consumption during operation, which is increasingly vital in today's energy-conscious environment. Their ability to respond swiftly to control signals enables smoother transitions and reduces wear and tear on mechanical components, leading to lower maintenance costs and longer equipment lifespan. Overall, the incorporation of servo drives into automation processes significantly boosts productivity and operational effectiveness.