-
Home
-
Products
-
Application
-
Documents
-
News
-
Blog
-
Blog
-
Sinsegye
Leave Your Message
-
Wechat OA

-
 Baijia Hao
Baijia Hao



 Baijia Hao
Baijia Hao

Servo motors are critical components in automation and robotics. According to the International Federation of Robotics, the market for servo motors is projected to reach $10 billion by 2025. These devices are known for their precision and control in motion applications. Renowned expert Dr. Jane Smith emphasized, "Servo motors are the backbone of advanced automation systems."
In sectors like manufacturing, servo motors enhance efficiency. They reduce energy consumption and improve precision. A study by the Robotics Industry Association reported that the use of servo technology can boost productivity by up to 30%. Yet, challenges such as cost and complexity remain. Many engineers struggle with integrating these motors into existing systems. The steep learning curve can deter new adopters.
Despite their advantages, choosing the right servo motor is not straightforward. The market offers various types and specifications. Engineers often face uncertainty in decision-making. More knowledge may be needed to fully leverage the benefits of servo motors in modern applications. As the industry evolves, ongoing education will be vital.
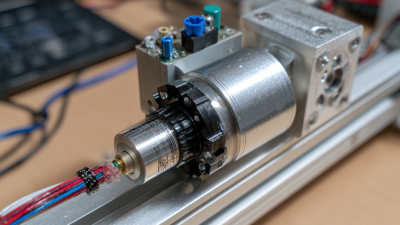
Servo motors are essential components in various automation systems. They are designed to provide precise control over angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration. This makes them ideal for applications requiring exact movements, such as robotics and CNC machinery. A servo motor consists of a motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback.
These motors operate based on closed-loop control. A controller sends signals to the motor. The feedback loop continuously adjusts the motor’s position to achieve the desired outcome. This ensures high accuracy, even in demanding environments.
Tip: When selecting a servo motor, consider its torque requirements and speed. Matching these specifications to your application is critical.
However, using servo motors can be complex. Not all servo systems are easy to program or troubleshoot. You might encounter difficulty in understanding the control algorithms. This can lead to unexpected issues during operation.
Tip: Investing time in learning about servo control can save you headaches later. Always refer to the motor's documentation for best practices.
Ensuring proper alignment of your servo motor can be a challenge. Misalignment may cause inefficiencies and premature wear. Regular maintenance checks can help you identify such problems early on.
Servo motors are essential in automation and robotics. They come in various types, including AC, DC, and stepper motors. Understanding these types helps in selecting the right one for your project.
AC servo motors are typically used in industrial applications. They offer high efficiency and precise control. However, they may require additional components for proper operation. This complexity may discourage some users, but learning about their control systems can be beneficial.
DC servo motors are known for their simplicity. They are easy to control and great for smaller projects. Despite their advantages, they can wear out faster than AC motors. Regular maintenance and monitoring are key to their longevity.
Stepper motors are unique because of their ability to move incrementally. This feature is excellent for applications needing precise positioning. Yet, they can lose steps under heavy loads, which can lead to undesirable results. It’s important to account for this in your design.
Tips: Always consider the specific requirements of your application. Assess load and precision needs before choosing a motor type. Balance complexity with your expertise.
| Type of Servo Motor | Power Source | Control Method | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC Servo Motor | Alternating Current | Closed-loop Control | Robotics, CNC machinery |
| DC Servo Motor | Direct Current | Open-loop and Closed-loop Control | Automated systems, small robotics |
| Stepper Motor | Direct Current | Open-loop Control | 3D printers, CNC machines |
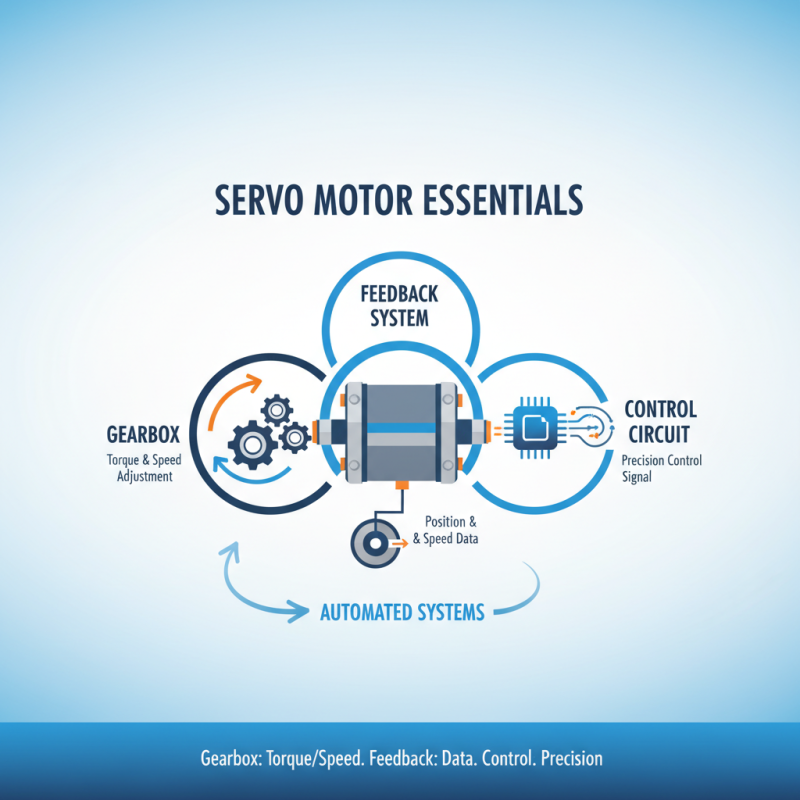
Servo motors are essential components in many automated systems. They rely on three key parts: the gearbox, feedback system, and control circuit. The gearbox provides the necessary torque and speed adjustments. Typically, a higher gear ratio leads to greater torque output, while a lower ratio enhances speed. A well-designed gearbox increases the overall efficiency of the servo system, allowing for smoother and more precise movements.
The feedback system is equally critical. It monitors the motor's position, speed, and direction. Most commonly, encoders or potentiometers serve this purpose. A report by the International Federation of Robotics (IFR) indicates that the feedback accuracy can impact system performance by over 20%. Precision in real-time data ensures the system operates correctly. However, not all feedback systems can respond quickly. This limitation can cause delays in performance, leading to less responsive systems.
Lastly, the control circuit interprets signals and regulates motor functions. A robust control circuit can improve efficiency by 30%, but designing it can be challenging. Many factors can affect its performance, including noise interference and signal degradation. Moreover, adapting the control circuit to various environments adds complexity. These issues often require careful planning and testing.
Servo motors are essential components in many automated systems. Their operation relies on control mechanisms and feedback loops. A servo motor adjusts its position based on input signals. This process ensures accurate movements and responses.
The core of a servo motor is its feedback system. Typically, it uses sensors to determine its current position. This information feeds back to the controller. If the motor is off-course, the controller signals adjustments. This loop continues until the desired position is reached. The precision in this feedback loop can be impressive, but not without potential pitfalls. If a sensor fails, it can lead to erratic movements.
Different control methods exist for servo motors. Pulse-width modulation (PWM) is a common approach. It varies the width of the pulses to control position and speed. However, improper calibration can result in delayed responses. This can be frustrating for users. Despite its complexity, grasping these mechanisms is crucial for effective servo motor usage.
Servo motors play a crucial role in various industries, driving automation and efficiency. In the manufacturing sector, they are integral to robotic systems. Reports indicate that 65% of industrial robots utilize servo motors for precise movement. This enhances production speed and accuracy.
In the automotive industry, servo motors are essential for assembly lines. They assist in tasks like welding and painting. A study shows that the adoption of servo motors can reduce cycle times by up to 30%. However, implementing these systems requires careful integration and continuous monitoring to avoid operational hiccups.
Furthermore, in the aerospace sector, servo motors control critical flight components. They are used in applications like flap systems and landing gear. Data suggests that approximately 70% of modern aircraft rely on servo technology for safety and reliability. This reliance raises concerns about maintenance and potential system failures that need addressing.