-
Home
-
Products
-
Application
-
Documents
-
News
-
Blog
-
Blog
-
Sinsegye
Leave Your Message
-
Wechat OA

-
 Baijia Hao
Baijia Hao



 Baijia Hao
Baijia Hao

The Siemens Servo Motor is a crucial component in modern automation. Known for its precision, it plays a significant role in various industrial applications. These motors excel in providing accurate position control and speed regulation.
Siemens Servo Motors operate through a closed-loop control system. This system constantly monitors feedback from the motor. It adjusts power supply to ensure optimal performance. This means the motor can respond quickly to changes, enhancing efficiency in production lines.
Understanding how Siemens Servo Motors function can lead to improved operations. However, their complexity may pose challenges for some users. It’s essential to grasp both their advantages and limitations. This knowledge allows for better troubleshooting and maintenance practices. By recognizing these factors, users can leverage the full potential of Siemens Servo Motors.
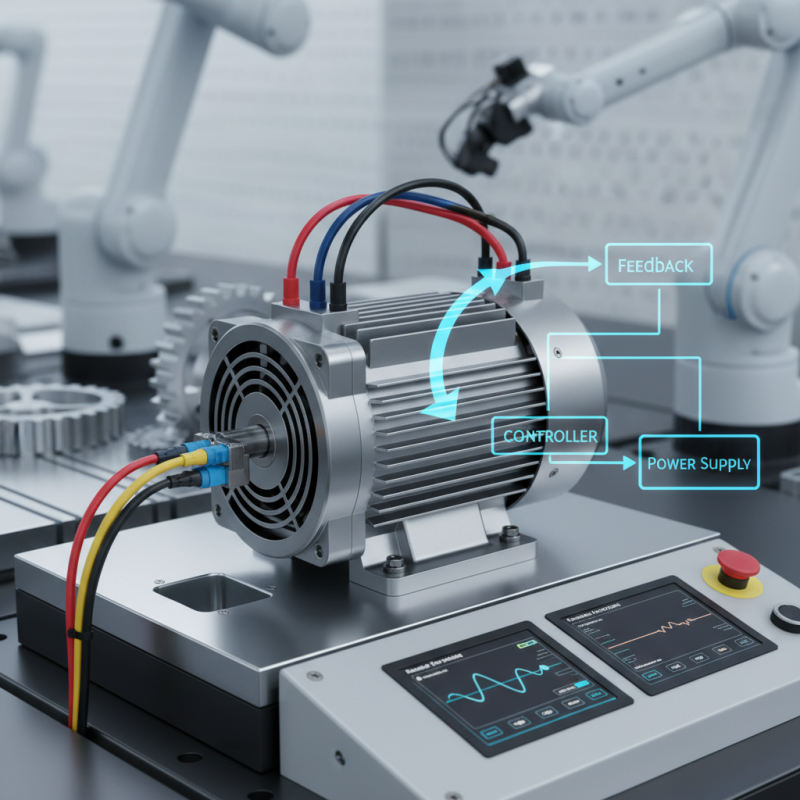
A servo motor is a specialized device that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. It is commonly used in automation and control systems. These motors enable precise control of angular position, speed, and acceleration. They are essential in robotics, CNC machinery, and other applications requiring accurate movements.
The inner workings of a servo motor are fascinating. It typically comprises a motor, a sensor for feedback, and a controller. The controller processes input signals, directing the motor to rotate to a specific angle. Sensors like encoders provide real-time feedback on position, ensuring the motor stays on target. However, achieving perfect control is a challenge. Calibration errors can happen. Feedback loops might not always respond quickly enough, leading to discrepancies.
In practical applications, these motors can face issues. Not all systems are designed to handle high torque or speed. Overheating can occur if not handled correctly. It’s critical to understand the limits of the motor and the system it is integrated into. Regular maintenance checks can help mitigate some of these risks. Keeping a close eye on performance helps identify problems before they escalate.
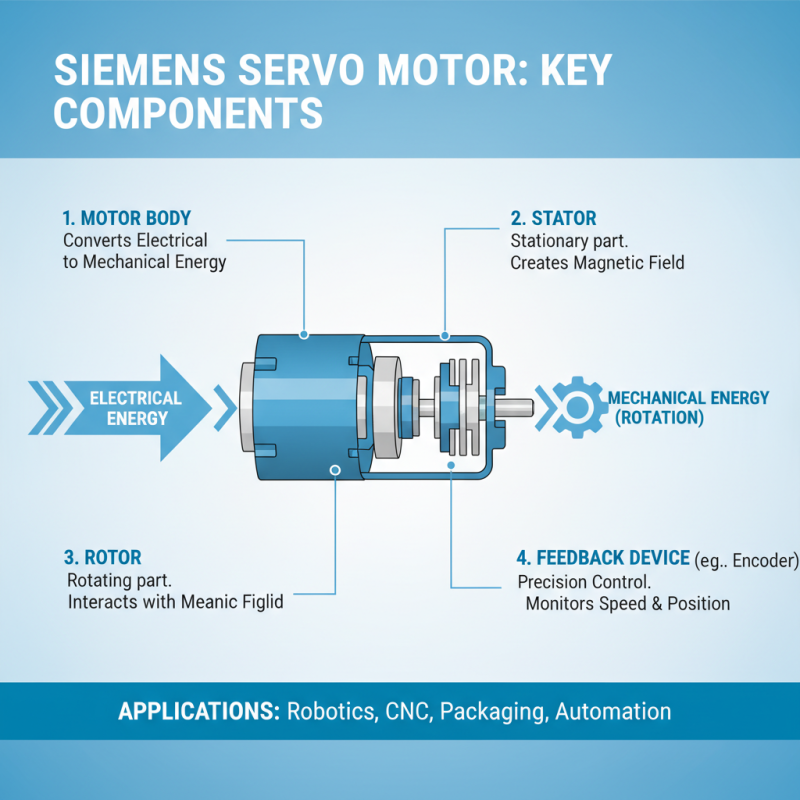
Siemens servo motors consist of several key components that enable effective control and precision in motion applications. At the core, the motor itself transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. This transformation is driven by a rotor and stator arrangement, which creates a magnetic field. The interaction between these components produces rotational movement.
Another crucial element is the feedback system. It often uses encoders to provide real-time position data. This allows for adjustments to be made quickly, enhancing accuracy. The control unit processes the feedback, ensuring the motor operates as intended. These adjustments can be complex, highlighting that not all setups run perfectly on the first try.
Power delivery is also vital. A servo drive controls the power sent to the motor. If the drive malfunctions, the entire system can be affected. Maintenance is key here, as wear and tear can lead to inefficiencies. Regular checks are essential to optimize performance. The integration of these components showcases the intricate design behind effective motion control solutions.
Siemens servo motors are widely used in various applications. They work based on a simple principle. A feedback loop controls the motor’s position or speed. This helps achieve high precision in movement. The motor receives commands and adjusts accordingly. It maintains performance through continual monitoring.
For example, a rotary encoder tracks the motor's position. This feedback is crucial. If the motor drifts from its desired path, it corrects itself rapidly. The closed-loop system ensures accuracy in tasks like robotics and CNC machines. However, it can be sensitive to disturbances. A small error can lead to performance issues.
Tips: Regularly check the encoder for accuracy. Even minor misalignments can affect operation. Calibrating the system can prevent larger problems. Consider testing in different loads. This will provide insights into performance limits. Understanding these principles can lead to better usage of servo motors.
Siemens servo motors play a crucial role in various industrial applications. They are essential in sectors like manufacturing, robotics, and automation. A recent market analysis indicates that the global servo motor market is expected to reach $16 billion by 2026, driven by rising automation demands.
In manufacturing, these motors help in precise control of machinery. They ensure accurate positioning, which is vital for tasks like assembly, welding, and packaging. For example, in robotic arms, servo motors enable smooth movements and increase operational efficiency.
Tips: When selecting a motor, consider torque needs and speed requirements. Each application may demand different specifications.
Another significant application is in CNC machinery. Siemens servo motors provide the necessary accuracy for machining operations. Furthermore, energy efficiency is another critical factor. Reports highlight that advanced servo systems can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%. Understanding the specific energy profile of your application is important.
Tips: Always analyze operational data to refine motor selection. Investing time here can enhance system performance.
Siemens servo motors are renowned for their precision and reliability. They incorporate advanced technology that offers numerous advantages. One significant benefit is their efficiency. A study showed that systems using servo motors can improve energy efficiency by up to 30%. This reduction in energy consumption is crucial, especially as industries focus on sustainability.
Another advantage is their performance in dynamic applications. These motors excel in situations requiring quick response and high torque. Reports indicate that servo motors can achieve speeds of up to 6,000 RPM, providing quick acceleration and deceleration. This capability enhances productivity in automation processes.
However, implementing servo motors is not without challenges. Initial costs can be high. The need for specialized knowledge can add complexity to deployment. Businesses must weigh these factors carefully. The choice of servo motors should align with specific project requirements and economic constraints. While the advantages are clear, potential drawbacks must prompt thoughtful consideration.